How air conditioning works
WHAT IT IS?
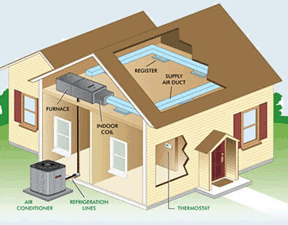
The most common central cooling system is a split system, which includes an outdoor cabinet containing a condenser coil and compressor, and an indoor evaporator coil, usually installed in conjunction with your furnace or air handler. The compressor pumps a chemical called refrigerant through the system.
Contact us for a free consultation
Make an appointment today for Residential AC Repair, Service, or Installation
Call 713-999-1900
HOW IT WORKS?
The warm air inside your home blows across the indoor evaporator coil and the heat energy from the air transfers to the refrigerant inside the coil. Think of the refrigerant like a sponge, absorbing the heat from the air. As a result, the air is now “cool”. The cooler air is circulated back through the home providing comfort. The refrigerant is pumped back to the compressor where the heat absorbed by the refrigerant is released and the cycle begins again. Moisture that contributes to humidity is also condensed out of the air.
Your cooling system is usually combined with your central heating system because they share the same ductwork for distributing conditioned air throughout your home.
FACTS:
- The typical central air conditioning system is a split system, with an outdoor air conditioning, or “compressor bearing unit” and an indoor coil, which is usually installed on top of the furnace in the home.
- Using electricity as its power source, the compressor pumps refrigerant through the system to gather heat and moisture from indoors and remove it from the home
- Heat and moisture are removed from the home when warm air from inside the home is blown over the cooled indoor coil. The heat in the air transfers to the coil, thereby “cooling” the air.
- The heat that has transferred to the coil is then “pumped” to the exterior of the home, while the cooled air is pumped back inside, helping to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature
- Central air conditioning can also be provided through a package unit or a heat pump.

